Improving Clinical Trial Knowledge and Referrals in NSCLC: Pilot Testing a Novel Healthcare IT Platform
Joshua Bauml, MD1, Victoria Sherry, CRNP1, Jun J. Mao, MD, MSCE1, Jessica Rearden, PhD, RN2, Susan Qi Li, MS1, William Dudley, PhD3, Karen Hammelef, DNP, RN4, Carrie T. Stricker, PhD, RN4, Corey J. Langer, MD1
1Abramson Cancer Center at the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, PA); 2University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Philadelphia, PA); 3Piedmont Research Strategies (Greensboro, NC); 4Carevive Systems, Inc. (Miami, FL).
Background
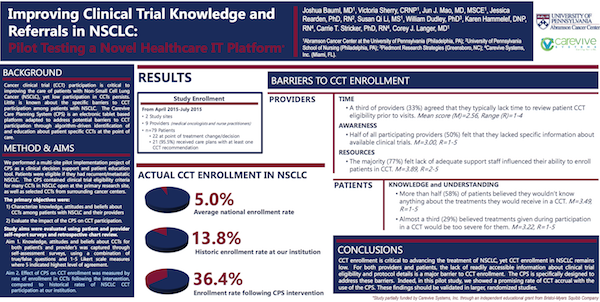
Cancer clinical trial (CCT) participation is critical to improving the care of patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), yet low participation in CCTs persists. Little is known about the specific barriers to CCT participation among patients with NSCLC. The Carevive Care Planning System (CPS) is an electronic tablet based platform adapted to address potential barriers to CCT participation through algorithm-driven identification of and education about patient specific CCTs at the point of care.
Method
We performed a multi-site pilot implementation project of CPS as a clinical decision support and patient education tool. Patients were eligible if they had recurrent/metastatic NSCLC. The CPS contained clinical trial eligibility criteria for many CCTs in NSCLC open at the primary research site, as well as selected CCTs from surrounding cancer centers.
The primary objectives were:
- Characterize knowledge, attitudes and beliefs about CCTs among patients with NSCLC and their providers
- Evaluate the impact of the CPS on CCT participation
Study aims were evaluated using patient and provider self-report surveys and retrospective chart review.
Aim 1. Knowledge, attitudes and beliefs about CCTs for both patient’s and provider’s was captured through self-assessment surveys, using a combination of true/false questions and 1-5 Likert scale measures where 5 indicated highest level of agreement.
Aim 2. Effect of CPS on CCT enrollment was measured by rate of enrollment in CCTs following the intervention, compared to historical rates of NSCLC CCT participation at our institution.




